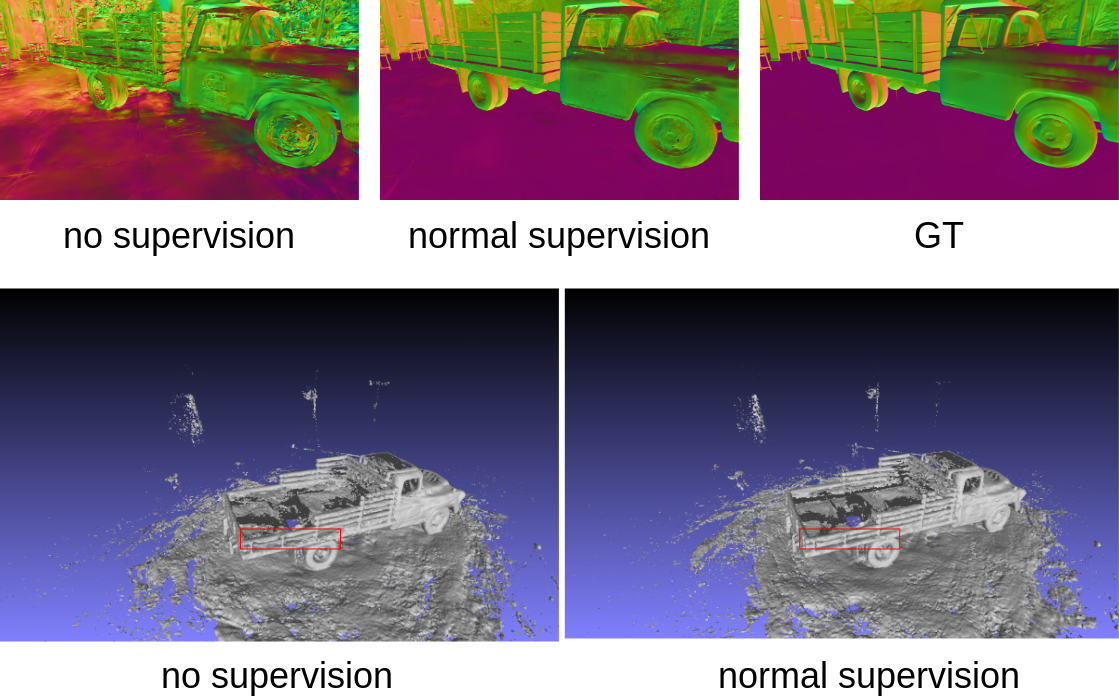
为点云渲染添加监督#
我们以表面法线为例,来说明如何为点云渲染模型添加表面法线先验的监督。所有的代码在example/supervise 文件夹下。
本教程用到的数据下载链接如下:
https://pan.baidu.com/s/1NlhxylY7q3SmVf9j29we3Q?pwd=f95m.
我们使用DSINE 模型来为 Tanks and Temple 数据集的truck场景生成Normal。
数据部分的修改#
由于Tanks and Temple 数据集为Colmap格式,因此我们选择继承Pointrix 中的Colmap Dataset进行修改。 为了读取DSINE 模型的Normal 先验输出,我们首先需要修改配置:
trainer.datapipeline.dataset.observed_data_dirs_dict={"image": "images", "normal":"normals"},
其中 normal 为存入Normal 的文件夹名称,normal为这个数据的变量名。
Pointrix 会根据当前数据路径和文件夹名称 依据后缀自动读取数据,相关的读取代码在Pointrix中展示如下:
1def load_observed_data(self, split):
2 """
3 The function for loading the observed_data.
4
5 Parameters:
6 -----------
7 split: str
8 The split of the dataset.
9
10 Returns:
11 --------
12 observed_data: List[Dict[str, Any]]
13 The observed_datafor the dataset.
14 """
15 observed_data = []
16 for k, v in self.observed_data_dirs_dict.items():
17 observed_data_path = self.data_root / Path(v)
18 if not os.path.exists(observed_data_path):
19 Logger.error(f"observed_data path {observed_data_path} does not exist.")
20 observed_data_file_names = sorted(os.listdir(observed_data_path))
21 observed_data_file_names_split = [observed_data_file_names[i] for i in self.train_index] if split == "train" else [observed_data_file_names[i] for i in self.val_index]
22 cached_progress = ProgressLogger(description='Loading cached observed_data', suffix='iters/s')
23 cached_progress.add_task(f'cache_{k}', f'Loading {split} cached {k}', len(observed_data_file_names_split))
24 with cached_progress.progress as progress:
25 for idx, file in enumerate(observed_data_file_names_split):
26 if len(observed_data) <= idx:
27 observed_data.append({})
28 if file.endswith('.npy'):
29 observed_data[idx].update({k: np.load(observed_data_path / Path(file))})
30 elif file.endswith('png') or file.endswith('jpg') or file.endswith('JPG'):
31 observed_data[idx].update({k: Image.open(observed_data_path / Path(file))})
32 else:
33 print(f"File format {file} is not supported.")
34 cached_progress.update(f'cache_{k}', step=1)
35 return observed_data
在使用Pointrix的自动数据读取功能后,我们需要对读取后的Normal数据进行处理。我们需要重载Colmap Dataset并修改其中的_transform_observed_data
函数来实现对读取观测数据 (表面法向) 的处理:具体代码在examples/gaussian_splatting_supervise/dataset.py.
1trainer:
2 datapipeline:
3 data_set: "ColmapDepthNormalDataset"
4 shuffle: True
5 batch_size: 1
6 num_workers: 0
7 dataset:
8 data_path: "/home/linzhuo/gj/data/garden"
9 cached_observed_data: ${trainer.training}
10 scale: 0.25
11 white_bg: False
12 observed_data_dirs_dict: {"image": "images", "normal": "normals"}
1# Registry
2@DATA_SET_REGISTRY.register()
3class ColmapDepthNormalDataset(ColmapDataset):
4 def _transform_observed_data(self, observed_data, split):
5 cached_progress = ProgressLogger(description='transforming cached observed_data', suffix='iters/s')
6 cached_progress.add_task(f'Transforming', f'Transforming {split} cached observed_data', len(observed_data))
7 with cached_progress.progress as progress:
8 for i in range(len(observed_data)):
9 # Transform Image
10 image = observed_data[i]['image']
11 w, h = image.size
12 image = image.resize((int(w * self.scale), int(h * self.scale)))
13 image = np.array(image) / 255.
14 if image.shape[2] == 4:
15 image = image[:, :, :3] * image[:, :, 3:4] + self.bg * (1 - image[:, :, 3:4])
16 observed_data[i]['image'] = torch.from_numpy(np.array(image)).permute(2, 0, 1).float().clamp(0.0, 1.0)
17 cached_progress.update(f'Transforming', step=1)
18
19 # Transform Normal
20 observed_data[i]['normal'] = \
21 (torch.from_numpy(np.array(observed_data[i]['normal'])) \
22 / 255.0).float().permute(2, 0, 1)
23 return observed_data
我们将处理后的Normal 数据存入observed_data 中后,Pointrix中的Datapipeline 会自动帮我们在训练过程中生产对应的数据,数据部分修改完成。
模型部分的修改#
首先,我们需要从Pointrix中导入基本模型,以便我们可以继承、注册和修改它们。
from pointrix.model.base_model import BaseModel, MODEL_REGISTRY
其中基本模型包含一个高斯点云模型,和一个相机模型。由于我们需要得到点云模型的表面法线,因此我们需要对高斯点云
模型进行对应的修改,从而使得其在forward函数前向输出表面法向,同时我们需要在get_loss_dict函数中获得对应的normal损失,使得normal监督
加入反向传播,并且
在get_metric_dict函数中得到渲染后的表面法向图片,为可视化预测表面法向做准备:
1@MODEL_REGISTRY.register()
2class NormalModel(BaseModel):
3 def forward(self, batch=None, training=True, render=True, iteration=None) -> dict:
4
5 if iteration is not None:
6 self.renderer.update_sh_degree(iteration)
7 frame_idx_list = [batch[i]["frame_idx"] for i in range(len(batch))]
8 extrinsic_matrix = self.training_camera_model.extrinsic_matrices(frame_idx_list) \
9 if training else self.validation_camera_model.extrinsic_matrices(frame_idx_list)
10 intrinsic_params = self.training_camera_model.intrinsic_params(frame_idx_list) \
11 if training else self.validation_camera_model.intrinsic_params(frame_idx_list)
12 camera_center = self.training_camera_model.camera_centers(frame_idx_list) \
13 if training else self.validation_camera_model.camera_centers(frame_idx_list)
14
15 point_normal = self.get_normals
16 projected_normal = self.process_normals(
17 point_normal, camera_center, extrinsic_matrix)
18
19 render_dict = {
20 "extrinsic_matrix": extrinsic_matrix,
21 "intrinsic_params": intrinsic_params,
22 "camera_center": camera_center,
23 "position": self.point_cloud.position,
24 "opacity": self.point_cloud.get_opacity,
25 "scaling": self.point_cloud.get_scaling,
26 "rotation": self.point_cloud.get_rotation,
27 "shs": self.point_cloud.get_shs,
28 "normals": projected_normal
29 }
30 if render:
31 render_results = self.renderer.render_batch(render_dict, batch)
32 return render_results
33 return render_dict
34 # 通过高斯点云的最短轴得到表面法向
35 @property
36 def get_normals(self):
37 scaling = self.point_cloud.scaling.clone()
38 normal_arg_min = torch.argmin(scaling, dim=-1)
39 normal_each = F.one_hot(normal_arg_min, num_classes=3)
40 normal_each = normal_each.float()
41
42 rotatation_matrix = unitquat_to_rotmat(self.point_cloud.get_rotation)
43 normal_each = torch.bmm(
44 rotatation_matrix, normal_each.unsqueeze(-1)).squeeze(-1)
45
46 normal_each = F.normalize(normal_each, dim=-1)
47 return normal_each
48
49 # 将高斯点云的表面法向投影到相机坐标系
50 def process_normals(self, normals, camera_center, E):
51 xyz = self.point_cloud.position
52 direction = (camera_center.repeat(
53 xyz.shape[0], 1).cuda().detach() - xyz.cuda().detach())
54 direction = direction / direction.norm(dim=1, keepdim=True)
55 dot_for_judge = torch.sum(direction*normals, dim=-1)
56 normals[dot_for_judge < 0] = -normals[dot_for_judge < 0]
57 w2c = E[:3, :3].cuda().float()
58 normals_image = normals @ w2c.T
59 return normals_image
60
61 def get_loss_dict(self, render_results, batch) -> dict:
62 loss = 0.0
63 gt_images = torch.stack(
64 [batch[i]["image"] for i in range(len(batch))],
65 dim=0
66 )
67 normal_images = torch.stack(
68 [batch[i]["normal"] for i in range(len(batch))],
69 dim=0
70 )
71 L1_loss = l1_loss(render_results['rgb'], gt_images)
72 ssim_loss = 1.0 - ssim(render_results['rgb'], gt_images)
73 loss += (1.0 - self.cfg.lambda_ssim) * L1_loss
74 loss += self.cfg.lambda_ssim * ssim_loss
75 # normal 监督的损失
76 normal_loss = 0.1 * l1_loss(render_results['normal'], normal_images)
77 loss += normal_loss
78 loss_dict = {"loss": loss,
79 "L1_loss": L1_loss,
80 "ssim_loss": ssim_loss,
81 "normal_loss": normal_loss}
82 return loss_dict
83
84 @torch.no_grad()
85 def get_metric_dict(self, render_results, batch) -> dict:
86 gt_images = torch.clamp(torch.stack(
87 [batch[i]["image"].to(self.device) for i in range(len(batch))],
88 dim=0), 0.0, 1.0)
89 rgb = torch.clamp(render_results['rgb'], 0.0, 1.0)
90 L1_loss = l1_loss(rgb, gt_images).mean().double()
91 psnr_test = psnr(rgb.squeeze(), gt_images.squeeze()).mean().double()
92 ssims_test = ssim(rgb, gt_images, size_average=True).mean().item()
93 lpips_vgg_test = self.lpips_func(rgb, gt_images).mean().item()
94 metric_dict = {"L1_loss": L1_loss,
95 "psnr": psnr_test,
96 "ssims": ssims_test,
97 "lpips": lpips_vgg_test,
98 "gt_images": gt_images,
99 "images": rgb,
100 "rgb_file_name": batch[0]["camera"].rgb_file_name}
101
102 if 'depth' in render_results:
103 depth = render_results['depth']
104 metric_dict['depth'] = depth
105
106 if 'normal' in render_results:
107 normal = render_results['normal']
108 metric_dict['normal'] = normal
109
110 if 'normal' in batch[0]:
111 normal = batch[0]['normal']
112 metric_dict['normal_gt'] = normal
113
114 return metric_dict
渲染部分的修改#
得益于Msplat 的多目标渲染,我们仅需要修改render_iter,即将点云模型输出的Normal特征加入渲染器即可, 同样,新修改后的渲染器需要
使用注册器注册,以便于我们通过配置来索引它。其中14行的Normals即为模型forward的输出参数,Pointrix
将自动对接:
1@RENDERER_REGISTRY.register()
2class MsplatNormalRender(MsplatRender):
3 def render_iter(self, height, width, extrinsic_matrix, intrinsic_params, camera_center, position, opacity,
4 scaling, rotation, shs, normals, **kwargs) -> dict:
5 direction = (position -
6 camera_center.repeat(position.shape[0], 1))
7 direction = direction / direction.norm(dim=1, keepdim=True)
8 rgb = msplat.compute_sh(shs.permute(0, 2, 1), direction)
9 extrinsic_matrix = extrinsic_matrix[:3, :]
10
11 (uv, depth) = msplat.project_point(
12 position,
13 intrinsic_params,
14 extrinsic_matrix,
15 width, height)
16
17 visible = depth != 0
18
19 # compute cov3d
20 cov3d = msplat.compute_cov3d(scaling, rotation, visible)
21
22 # ewa project
23 (conic, radius, tiles_touched) = msplat.ewa_project(position, cov3d,
24 intrinsic_params,
25 extrinsic_matrix,
26 uv,
27 width,
28 height,
29 visible
30 )
31
32 # sort
33 (gaussian_ids_sorted, tile_range) = msplat.sort_gaussian(
34 uv, depth, width, height, radius, tiles_touched
35 )
36
37 Render_Features = RenderFeatures(rgb=rgb, depth=depth, normal=normals)
38 render_features = Render_Features.combine()
39
40 ndc = torch.zeros_like(uv, requires_grad=True)
41 try:
42 ndc.retain_grad()
43 except:
44 raise ValueError("ndc does not have grad")
45
46 # alpha blending
47 rendered_features = msplat.alpha_blending(
48 uv, conic, opacity, render_features,
49 gaussian_ids_sorted, tile_range, self.bg_color, width, height, ndc
50 )
51 rendered_features_split = Render_Features.split(rendered_features)
52
53 normals = rendered_features_split["normal"]
54
55 # convert normals from [-1,1] to [0,1]
56 normals_im = normals / normals.norm(dim=0, keepdim=True)
57 normals_im = (normals_im + 1) / 2
58
59 rendered_features_split["normal"] = normals_im
60
61 return {"rendered_features_split": rendered_features_split,
62 "uv_points": ndc,
63 "visibility": radius > 0,
64 "radii": radius
65 }
利用Hook 函数添加相关的日志#
最后,我们希望每次验证过程中,可视化模型预测的表面法向图片,因此我们需要修改对应的钩子函数,来达到每次验证后可视化表面法向的效果:
1@HOOK_REGISTRY.register()
2class NormalLogHook(LogHook):
3 def after_val_iter(self, trainner) -> None:
4 self.progress_bar.update("validation", step=1)
5 for key, value in trainner.metric_dict.items():
6 if key in self.losses_test:
7 self.losses_test[key] += value
8
9 image_name = os.path.basename(trainner.metric_dict['rgb_file_name'])
10 iteration = trainner.global_step
11 if 'depth' in trainner.metric_dict:
12 visual_depth = visualize_depth(trainner.metric_dict['depth'].squeeze(), tensorboard=True)
13 trainner.writer.write_image(
14 "test" + f"_view_{image_name}/depth",
15 visual_depth, step=iteration)
16 trainner.writer.write_image(
17 "test" + f"_view_{image_name}/render",
18 trainner.metric_dict['images'].squeeze(),
19 step=iteration)
20
21 trainner.writer.write_image(
22 "test" + f"_view_{image_name}/ground_truth",
23 trainner.metric_dict['gt_images'].squeeze(),
24 step=iteration)
25
26 trainner.writer.write_image(
27 "test" + f"_view_{image_name}/normal",
28 trainner.metric_dict['normal'].squeeze(),
29 step=iteration)
30 trainner.writer.write_image(
31 "test" + f"_view_{image_name}/normal_gt",
32 trainner.metric_dict['normal_gt'].squeeze(),
33 step=iteration)
最后,我们需要修改我们的配置,从而将修改后的模型,渲染器,数据集,钩子函数添加到Pointrix 训练流中:
Warning
如果您在Basemodel 基础上新加入了可学习的参数(例如卷积网络或者MLP),请在optimizer配置中添加对应的可学习的参数,这样新参数才会优化。
1name: "garden"
2
3trainer:
4 output_path: "/home/linzhuo/clz/log/garden"
5 max_steps: 30000
6 val_interval: 5000
7 training: True
8
9 model:
10 name: NormalModel
11 lambda_ssim: 0.2
12 point_cloud:
13 point_cloud_type: "GaussianPointCloud"
14 max_sh_degree: 3
15 trainable: true
16 unwarp_prefix: "point_cloud"
17 initializer:
18 init_type: 'colmap'
19 feat_dim: 3
20 camera_model:
21 enable_training: False
22 renderer:
23 name: "MsplatNormalRender"
24 max_sh_degree: ${trainer.model.point_cloud.max_sh_degree}
25
26 controller:
27 normalize_grad: False
28
29 optimizer:
30 optimizer_1:
31 type: BaseOptimizer
32 name: Adam
33 args:
34 eps: 1e-15
35 extra_cfg:
36 backward: False
37 params:
38 point_cloud.position:
39 lr: 0.00016
40 point_cloud.features:
41 lr: 0.0025
42 point_cloud.features_rest:
43 lr: 0.000125 # features/20
44 point_cloud.scaling:
45 lr: 0.005
46 point_cloud.rotation:
47 lr: 0.001
48 point_cloud.opacity:
49 lr: 0.05
50 # camera_params:
51 # lr: 1e-3
52
53 scheduler:
54 name: "ExponLRScheduler"
55 params:
56 point_cloud.position:
57 init: 0.00016
58 final: 0.0000016
59 max_steps: ${trainer.max_steps}
60 datapipeline:
61 data_set: "ColmapDepthNormalDataset"
62 shuffle: True
63 batch_size: 1
64 num_workers: 0
65 dataset:
66 data_path: "/home/linzhuo/gj/data/garden"
67 cached_observed_data: ${trainer.training}
68 scale: 0.25
69 white_bg: False
70 observed_data_dirs_dict: {"image": "images", "normal": "normals"}
71
72 writer:
73 writer_type: "TensorboardWriter"
74
75 hooks:
76 LogHook:
77 name: NormalLogHook
78 CheckPointHook:
79 name: CheckPointHook
80
81 exporter:
82 exporter_a:
83 type: MetricExporter
84 exporter_b:
85 type: TSDFFusion
86 extra_cfg:
87 voxel_size: 0.02
88 sdf_truc: 0.08
89 total_points: 8_000_000
90 exporter_c:
91 type: VideoExporter
经过上述修改(所有代码的高亮部分),我们即完成了对高斯点云表面法向的监督。所有的代码在example/supervise 文件夹下。
我们通过下面的命令运行代码:
python launch.py --config colmap.yaml trainer.datapipeline.dataset.data_path=your_data_path trainer.datapipeline.dataset.scale=0.5 trainer.output_path=your_log_path
实验结果如下: